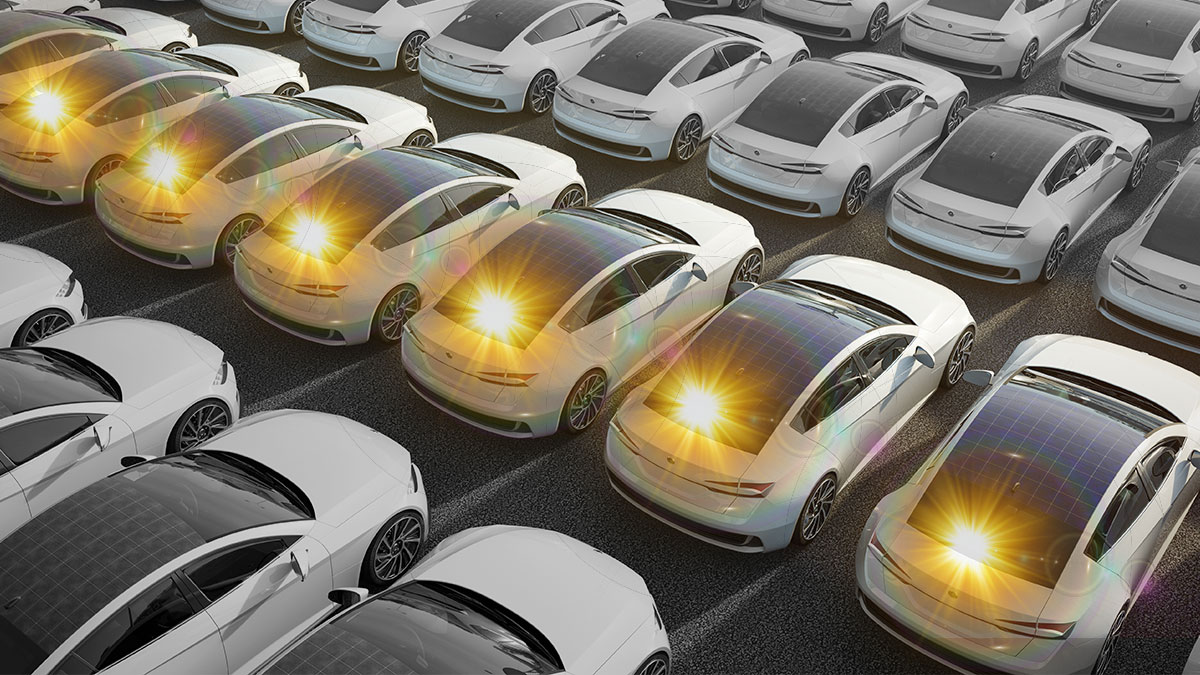
6 Shining New Examples of Integrated Photovoltaics (PV)
Climate change policies around the world are working to enable green growth through the use of sustainable energy. More than 70 countries, including the biggest polluters, China, the United States, and the European Union, have set net-zero targets, covering about 76% of global emissions.1
President Biden set a goal for the U.S. to achieve carbon pollution–free electricity by 20352.
Solar energy will play the most prominent role of all sustainable energy sources in accomplishing these goals, because solar is arguably the cheapest and most innovative renewable energy available3.
Photovoltaic (PV) energy is electricity derived from the sun’s energy. Efficient, cost-effective, accessible, and sustainable, modern photovoltaics convert light into electricity at the atomic level4.
Traditionally, desert conditions have been the optimal environment for PVs to absorb the photons of light needed to release electrons and ultimately create electric currents that can be used as electricity5. But times have changed, and PVs are being integrated into surprising new applications, including these six examples highlighted below.

Source & Permission: Fraunhofer ISE 2022
- Vehicle-Integrated PV (VIPV): Self-Charging Solar-Powered Cars
Vehicles can be encased in solar panels that allow them to self-charge. One such example is Germany’s Sono Motors Sion vehicle. These cars can drive 25 miles per day without recharging. The technology has potential for future use in buses, trucks, trains, and even boats.
- Agrivoltaics: Agricultural-Integrated Panels
As solar panels heat up, their efficiency decreases. By cultivating crops underneath agrivoltaic PV panels, researchers can reduce the panels’ temperature. The shade provided by solar panels may also allow the soil to retain more water, so less irrigation is needed. Agricultural integrated panels also help protect crops from high winds and extreme weather6.
- Road-Integrated PV (RIPV): Panels in Highway Infrastructure
Noise-protection barriers are a remarkable technology that can combine the function of blocking noise pollution and reducing carbon dioxide emissions while generating clean energy. These solar cells convert sunlight into electricity on both sides, and their vertical installation inspires new possibilities for future use. Future innovations include PV highway panels that can reduce air pollution.
- Floating PV (FPV): Solar Panels on Water
A floating PV system is placed directly on top of a body of water instead of on land or a rooftop. They are often placed on reservoirs and artificial lakes to protect the panels from damage from tides or saltwater corrosion. Floating solar can be up to 15% more efficient than land-based solar due to water’s cooling effects7.
- Urban PVs
PVs can be incorporated into the urban environment with smart technology that integrates them and links them to the grid – for example, within furniture and fixtures like bus stops or sidewalks. Around half the total annual electricity demand in the Netherlands can be generated using urban PVs8.
- Building-Integrated PVs (BIPV)
Building-integrated PVs are increasingly used in construction design and planning. They can be incorporated into walls and roofs or even retrofitted. Or they can be connected to the power supply of the building itself. The CityWave building in Milan, Italy, will be entirely powered by renewables, with 36,089 square feet of PV panels on its roof regenerating some 1.2 gigawatts of energy per year9.
This market expansion leads to a broad diversification in PV module technology. Although most of the market uses crystalline silicon technology, thin-film cells like cadmium telluride (CdTe) or copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) are also used.
Researchers are also looking into passivated emitter and rear cell (PERC) and heterojunction (HJT) solar panels. Both have advantages and challenges that require research and further investigation, but it’s possible that these might become the dominant cell technologies of the future.
Read more about the solar materials industry in our white paper – Challenges And Trends For Emerging Solar Cell Technologies
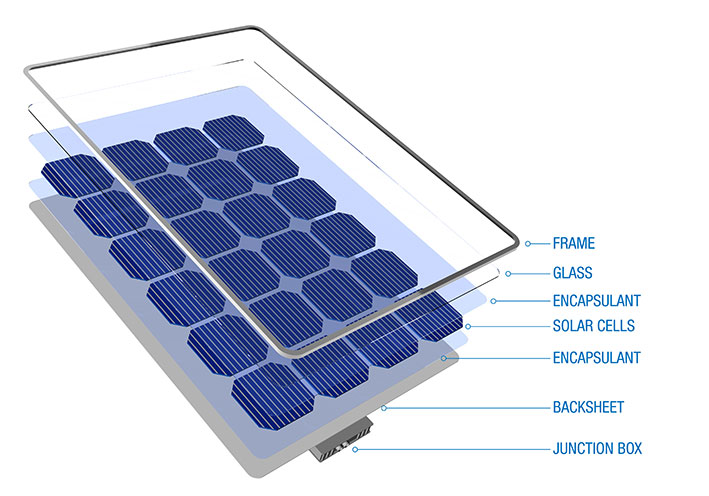
Typical Applications in the Solar Industry
The solar market is flourishing, and a diversity of manufacturers, researchers, and innovators currently face a number of challenges. PerkinElmer has instruments to help innovators get the most from solar technology, save money, streamline processes, and ensure effective quality control.
Find out more about our Analytical Solutions here
NOTES:
1. https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/net-zero-coalition
2. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2021/04/22/fact-sheet-president-biden-sets-2030-greenhouse-gas-pollution-reduction-target-aimed-at-creating-good-paying-union-jobs-and-securing-u-s-leadership-on-clean-energy-technologies/
3-6. Challenges & Trends for Emerging Solar Cell Technologies. (2022) [whitepaper] Oreski, Wita.
7. https://www.eesi.org/articles/view/floating-a-new-solution-for-solar-deployment
8. https://d1rkab7tlqy5f1.cloudfront.net/Websections/Urban%20Energy/TUDelft-SolarUrban-Final.pdf
9. https://www.theb1m.com/article/work-begins-on-solar-powered-gateway-to-milan

