The Importance of “Industry 4.0” Strategies for GC Labs
The saying “necessity is the mother of invention” certainly applies to Industry 4.0., or what some experts call “the fourth industrial revolution.” In pre-pandemic times, interest in the potential of smart technologies was high-but it took a pandemic to truly force innovation to the forefront. Demands for social distancing, work-from-home, a hybrid workforce, and labor shortages have accelerated interconnectivity and smart automation.
Industry 4.0 is transforming manufacturing by creating digital connections among industry, businesses, and other processes using smart and autonomous systems fueled by data and machine learning. Although the initial focus of Industry 4.0 was on manufacturing, many other businesses have begun adopting 4.0 strategies—including laboratories.
Laboratory 4.0 is increasing across the many different types of labs operating today. For example, an average chemical QC lab can reduce costs by as much as 45% through digital enablement alone. The shift to Laboratory 4.0 is a steady push to innovate by bringing data-driven processes and operational flexibility to the lab.
Labs working with GC (gas chromatography) are facing higher demands for productivity while still feeling pressure to reduce costs. While digitalization is well underway in the manufacturing sector, laboratories often lag, relying upon manual work – which brings with it the related consequences of human error. This is the first in a series of three posts covering the shift to Industry 4.0 for laboratories conducting gas chromatography analyses.
The Evolution of Industry—From Mechanical Production to Cyber-Physical Systems
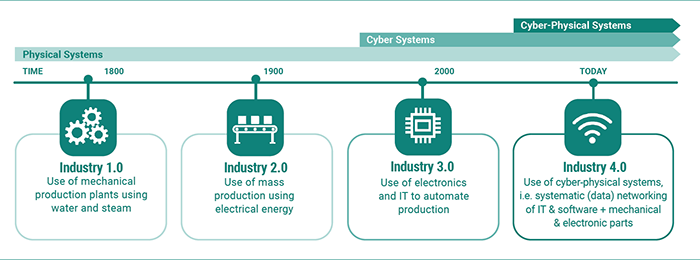
Industry 4.0 began in the first and second decades of the 21st century. Those years saw unprecedented advances in computing power and internet connectivity. Manufacturing industries use those advances to transform their operations through automated and interconnected processes that increase efficiency and output. As a result, smart manufacturing operations continue to seamlessly combine the digital and physical worlds in time and cost-saving, disaster-averting, productivity-boosting ways.
Companies using Industry 4.0 technologies before COVID-19 found themselves better positioned to respond to the crisis. It is now proven that Industry 4.0 innovation can be utilized to future-proof today’s labs. Remote monitoring, remote programming, and predictive maintenance solutions or live status notifications are easy to implement and allow labs to reduce downtime, improve performance, and support business continuity. Remote access systems and predictive maintenance tools empower lab operators to combine the digital and physical worlds in time and cost-saving, disaster-averting, productivity-boosting ways.
How Digital Enablement Can Be Implemented in Laboratories Using GC
Digitally-enabled labs can take advantage of wireless devices, managing the analytical workflow remotely: the physical space is merged with the digital one enabling a revolutionized user experience. In addition, real-time data analytics and ongoing analysis verification allow labs to have the full analytical workflow under control while being able to optimize it and prevent unexpected mishaps.
The PerkinElmer GC 2400™ Platform features a web app that can be used to monitor and control the workflow from any PCs or wireless device, a detachable touchscreen that staff can use to monitor and control a GC 2400™ System or multiple systems remotely from any location in the lab. This type of ingenuity supports the transition to digital enablement for GC.
Digital enablement is also useful for managing and storing lab information and data. Labs are now harmonizing multiple software systems to create a digitally integrated approach that allows multi-user access. Although seamlessly integrating numerous software systems is the ideal approach, it can also be challenging to accomplish.
Examples of an effectively integrated software system are seen in the features of the GC 2400 Platform. The platform is controlled and managed by the SimplicityChrom CDS Software, which supports multiple user accounts and profiles, allowing workflow to be directly managed by its analyst and managed within the same system. These efficiencies simplify the administration process and mitigate many common IT challenges associated with multiple domain management.
Remote monitoring systems also boost productivity and accelerate the pace of innovation by improving the process of monitoring laboratory instruments and environmental conditions. With a product such as Asset Genius®, labs can optimize their time by automating the collection, visualization, and reporting of many critical lab assets. 24/7 monitoring and alert notifications help labs gain peace of mind and confidence in the assets – and the lab environment.
Interested to learn more about how digital enablement can drive the implementation of Industry 4.0 in the lab, with a focus on GC? Download the article.
Notes:
- IBM. What is Industry 4.0? – https://www.ibm.com/topics/industry-4-0
- LabMate Online. 2022. What is Laboratory 4.0? – https://www.labmate-online.com/news/laboratory-products/3/breaking-news/what-is-laboratory-40/57352
- McKinsey & Company. 2019. Digitization, automation, and online testing: The future of pharma quality control. – https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/life-sciences/our-insights/digitization-automation-and-online-testing-the-future-of-pharma-quality-control
- McKinsey & Company. 2021. Digitization, automation, and on line testing: Embracing Smart Quality Control.- https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/life-sciences/our-insights/digitization-automation-and-online-testing-embracing-smart-quality-control

